 |
| free-15-small-business-profit-and-loss-samples-in-excel |
FREE 15+ Small Business Profit and Loss Samples in Excel
What is a profit and loss statement for a small business?
A profit and loss statement is at the heart of small business accounting. A profit and loss statement describes a company's revenue and expenses over a period of time. An income statement, profit statement, statement of operations, or profit and loss report are several terms for the same thing. Whatever term is used to describe this financial statement, it is a snapshot of a company's income and expenditures over a period of time.
This is usually done at least once a quarter and once a year, though it can be done more frequently. Profit and loss statements are typically produced on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis.
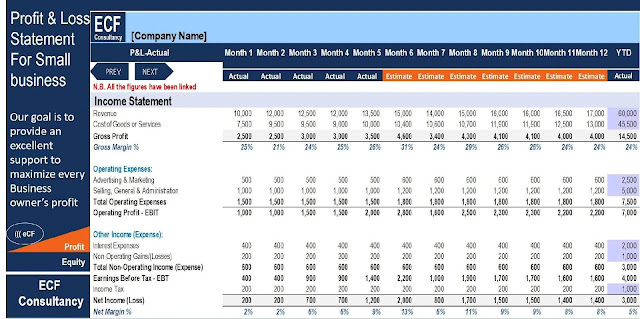
A profit and loss statement for a small firm
Revenues and costs are broken down by line item and compared to previous quarters to find positive and negative company trends. A Profit and Loss Template for Small Businesses may help you create the framework you need to ensure that you have a well-prepared and reliable statement on hand. You can do so by selecting one of the outstanding templates shown above. If you wish to write it yourself, use the following steps as a guide:
1. Start with the money.
Revenue is the first item on a profit and loss statement for small businesses, and it covers all income components. Sales, gross revenues, fees, or any other term used to describe the company's operating revenue could be used here. When using the accrual method of accounting, revenue is recorded as it is produced at the time of sale, even if payments have not yet been received. Revenues are reported when payment is received while employing the cash method.
2. Make a list of your expenses.
The expense portion of a profit and loss statement for small businesses contains any costs incurred to manage the business. When accounting for various costs, it is necessary to understand asset depreciation. Certain purchases, such as office equipment, must be capitalized and depreciated during the item's useful life. Every year, the profit and loss statement shows 20% of the cost of the equipment.
3. Fill in the blanks with your gross earnings.
The gross profit is the difference between revenue or gross revenues and the cost of products sold. The gross profit and gross revenues are equivalent if the company is a service business with no inventory.
4. Determine the profit and loss.
The net amount equals a company's profit or loss for the period after deducting any taxes owing from pretax income. Net profit or loss is commonly equated to profits before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization when comparing firms in various industries and tax situations, or when exact data aren't yet available.
Download also:

Post a Comment